HRV Score Different Than Other Apps
Different Scales for HRV Scores
Our HRV score is based on the Time Domain rMSSD calculation – which is heavily researched and many other apps use as their base as well. Other apps that make use of rMSSD apply a seemingly random multiplier to the natural log of rMSSD to get most people near a 100 range. The problem on the other systems is that many people end up scoring well over 100 and everyone’s scores are artificially high (if the target range is 0 to 100).
We’ve used the millions of readings in our database to make sure that everyone fits within the 0 to 100 score (including elite athletes). This means that compared to some other systems our HRV score might seem lower, but it is true to the 0 to 100 scale.
The important thing to note is that the HRV score itself doesn’t mean anything except when compared to others on the same platform or against yourself over time. For universally comparable numbers, the unscaled rMSSD and ln(rMSSD) values should be consistent across any system or any body of research. This is why we provide the raw numbers with our readings as well.
Note that readings of different durations, i.e. 5 minutes vs. 20 minutes should not be compared. You'll find that when searching for HRV data, the length of reading is almost always specified, and more often than not, you'll find the data collected was in 5 minute or even shorter readings. "Because of their relative ease of recording, short-term measurements have been widely used and studied for many years, and appear to be the most commonly found source of published HRV data." Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5624990/#S24title
We have some users who measure their HRV overnight with another system (like Whoop or Oura) as well as take their Morning Readiness HRV every morning. They analyze the data separately and draw conclusions from both. We recommend keeping the overnight HRV data and Morning Readiness HRV data separate because "there are considerable changes in the spectral analysis of cardiac function occurring during different sleep stages and between sleep cycles across the night. Hence, time of night and sleep stage need to be considered when reporting any HRV differences." Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7046589/
What if you are comparing the rMSSD and ln(rMSSD) values across platforms and still see differences?
Research standardized calculations such as rMSSD can still appear slightly different between systems. This could be due to differences in hardware (heart rate monitors, etc.) or recommended measurement duration and positions. But it is usually due to differences in the way misreads and signal noise (referred to as artifacts) are handled. On the software side we calculate out misreads and signal noise as best as possible in a process using artifact cleaning algorithms. Each system has their own method and algorithms for addressing these misreads (and some systems don’t even do this). This could potentially cause the same inputs and HRV calculations to produce different final results. To minimize the possibility of misreads from your heart rate monitor please ensure the following:
- Thoroughly moisten the chest strap
- Tighten or loosen the strap to ensure it does not move across the skin during the reading
- Make sure the battery in the strap is not low
Please note that readings of different durations should not be compared, nor should readings taken at rest in routine, planned circumstances be compared to readings sampled at random throughout the day. Please see this article for more explanation: Why HRV Morning Readiness?
If you are importing the raw RR intervals into Kubios and still see differences in the calculated data, there are a few things to note. The raw RR intervals collected by our app from your heart rate sensor go through an artifact cleaning algorithm, then the calculations are made (RMSSD, etc.).
Kubios has several artifact cleaning algorithms you can select. It would be a good exercise to check the reading results on our app to see how many artifacts were detected and corrected: Signal Quality: Raw vs Corrected R-R Intervals
Then choose an artifact cleaning algorithm in Kubios and see how close the results are. Our algorithm is proprietary and we do not have the ability to share it, but you might find that some of the available algorithms in Kubios match more closely to ours than others.
Elite HRV Scores Compared To Other Platforms
We thought it might be helpful to show how Elite HRV’s normal demographic values translate to other platforms.
Keep in mind, the data used to calculate these scores was gathered on Elite HRV’s platform, so it does not necessarily represent the user populations of those other platforms and does not take into account different artifact cleaning algorithms and other potential differences. There are other HRV software applications that are not listed in the below table because they either do not publish their scoring system or do not have a large user base.
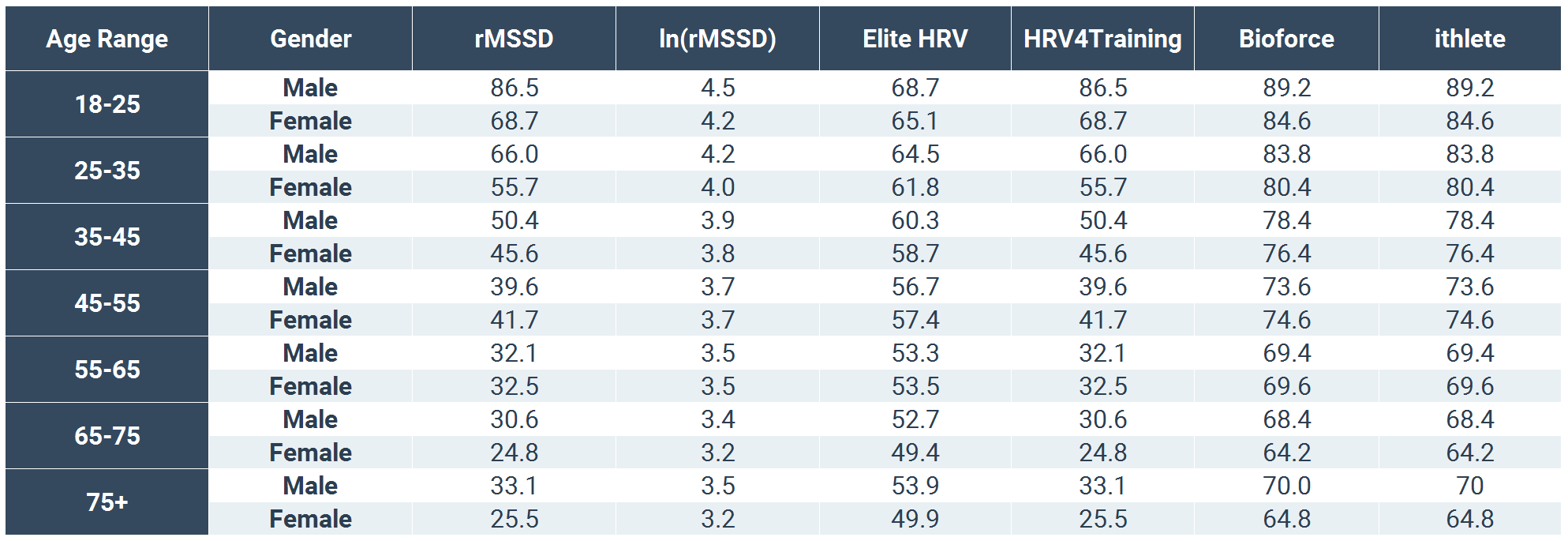
Table 1 – Data gathered on Elite HRV platform shows rMSSD, ln(rMSSD), and “HRV Scores” for Elite HRV and is calculated for other HRV software applications based on published calculations. The data does not necessarily represent the user populations for the other HRV platforms.
Apple Health Specifics
Your HRV score on Elite HRV and the one that shows up when you are linked to Apple Health will be different. Apple Health's "HRV" slot is asking for SDNN (which is a particular Time Domain measure of HRV). Our HRV score is based on RMSSD (a different Time Domain measure of HRV). So when we send the one that Apple Health is designed to receive, it changes the score.
